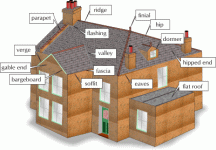
Unfamiliar with roofing terms? Here’s a list of that will help you understand your roof:
Alligatoring
Surface cracking due to oxidation and shrinkage stresses, which shows as repetitive mounding of an asphalt surface, resembling the hide of an alligator.
Asphalt
A dark brown to black substance that is found in nature and is also a residue in petroleum or coal tar refining that consists chiefly of hydrocarbons.
Asphalt Primer
A solution of asphalt in petroleum solvent, used to prepare concrete roof decks for the application of hot asphalt. The primer lays dust and improves the adhesion of the molten asphalt to the roof deck.
Base Flashing
The portion of the flashing that is attached to or rests on the roof deck to direct the flow of water on the roof, or to seal against the roof deck.
Base Sheet
A heavy sheet of felt sometimes used as the first ply in built-up roofing.
Bitumen
Bitumen is mixtures of hydrocarbons of natural or refining origin, which may be gaseous, liquid, or solid. In the roofing industry the word covers both asphalt and coal tar pitch.
Blind nailing
Shingles nailed in such a location that when the next shingle is applied, the nails of the first shingle do not show.
Blisters, structural
The more evident and more serious blisters are structural blisters. They are caused mainly by the expansion of trapped air and water -vapor or moisture or other gases.
Block method
The method of applying shingles in vertical rows from eave to peak rather than in horizontal rows from rake to rake. It is not a recommended method.
Blueberry
These are small surface blisters, which can be seen in large numbers over the entire roof area, more predominant during warm weather where roofs are exposed directly to the sun, and which are a result of natural weathering of the surface bitumen.
Bond
Adherence between plies of felt, or between felts and other elements of roof systems.
Breather
A type of roof vent consisting of a hooded flanged pipe 2″ to 8″ in diameter, penetrating the roofing membrane to allow escape of moisture from insulation.
Buckling
Warping or wrinkling of the roof membrane.
Built-up Roofing
A built-up roofing consists of plies or layers of roofing felt bonded together on site with hot bitumen. A protective surface coating of gravel or slag is sometimes embedded in a heavy top coating of hot bitumen.
Cant Strip
A beveled support used at the intersection of the roof deck with vertical surfaces so that bends in the roofing membrane to form base flashings can be made without breaking the felts
Cap Flashing
That portion of the flashing built into a vertical surface to prevent the flow of water behind the base flashing.
Cement Asphaltic Plastic
A mixture of asphalt, solvent and mineral stabilizer used for example to adhere flashings or to fill pan flashings.
Coal Tar Pitch
A bituminous material produced by distilling crude tar residue derived from the cooking of coal. It is used as the waterproofing material for tar and gravel built-up roofing.
Collar
A metal cap flashing around a vent pipe projecting above a roof deck.
Conductor
A pipe for conveying rainwater from a roof gutter to a drain, or from a roof drain to a storm drain.
Coping
The cap or highest covering course of a wall, usually overhanging the wall and having a sloping top to carry off water.
Counter flashing
Strips of metal, roofing, or fabric inserted and securely anchored to the reglet or attached to a vertical surface above the plane of the roof and turned down over the face flashing to protect the base flashing.
Cut Back
A solution of bitumen in a volatile solvent. Cut backs are used as primers, cold application cementing agents, and damp roofing coatings.
Cutout
The slot between shingle tabs to create the distinctive 2 or 3 tab appearance.
Dead load
The total weight of all installed materials and the constant weight of a roof used to compute the strength of all supporting framing members.
Deck
The structural roof to the top surface of which a roof covering system is applied.
Double pour
The application of the top coating of bitumen and the gravel surfacing of a built-up roofing in two separate applications, used on dead level roofs, particularly when the roof is designed for flooding with water.
Downspout
A pipe for conveying rainwater from a roof gutter to a drain, or from a roof drain to a storm drain.
Drip edge
A modified L-shaped flashing used along the eaves and rakes. The drip edge directs runoff water into the gutters of air and away from the fascia.
Eave
The horizontal roof overhang that extends outward and is not directly over the exterior walls or the building’s interior.
Emulsified Asphalt
Straight run asphalt liquefied by clay emulsifiers and water.
Expansion joint
A planned, controlled joint placed between two roof surfaces or between two sections of a built-up roof. The expansion joint allows the roof to expand without physical damage to the roof or the building.
Exposure
That portion of a shingle that is exposed to the weather.
Face nailing
Nailing with the nails placed in the exposed area or face of the shingle.
Felt
A very general term used to describe roll roofing materials, consisting of a mat of organic or inorganic fibers unsaturated, saturated, or saturated and coated with asphalt or coal-tar pitch. Types include: Asbestos, Asphalt Saturated, Coated, Glass, No. 15, Perforated, Rag, and Tar Saturated.
Fill
Lightweight concrete placed on a level roof deck in varying thickness’ to build slopes to the roof drains.
Fire Rating System for classifying the fire resistances of various materials. Roofing materials are rated Class A, B or C, with Class A materials having the highest resistance to fire originating outside the structure
Flashing
Metal strips used to form a watertight seal between the items butted up against the shingles. Flashing is used along walls, chimneys, and dormers.
Flashing block
A specially designed masonry block having a slot or opening into which the top edge of the roof flashing can be inserted and anchored. Also known as raggle block
Glaze Coat
A mopping of bitumen on exposed felts to protect them from the weather pending completion of the job.
Gravel stop
A gravel guard used at the rakes and eaves of a built-up gravel coated roof.
Head lap
The overlapping of shingles or roofing felt at their top edge. Roofing felt should be head lapped by a minimum of 2 in.
Hot Asphalt Temperature Application or EVT
Equiviscous Temperature or EVT. EVT is expressed as a range, typically a 50 degree (F) range. It fluctuates depending upon the particular asphalt being applied. Kettle temperature therefore varies so to ensure the hot liquid asphalt is the correct temperature at the point of application. So, if a particular asphalt has an EVT of 450 degrees (F) you may see kettle temperatures over 500 degrees (F) depending on the distance from the kettle to point of application.
Ice dam
A build-up of ice at the eaves drainage area or in the valley of a sloping roof. An ice dam is very harmful since it prevents melting snow or rainwater from exiting the roof, and the water backs up under the shingles instead.
Jack
A flanged metal sleeve used as part of the flashing around small items that penetrate a roof.
Lock Shingles
Designed with a mechanical locking feature to provide effective wind resistance.
Louvers Slatted devices installed in a gable or soffit (the underside of eaves) to ventilate the space below a roof deck and equalize air temperature and moisture.
Membrane
A saturated cotton or burlap fabric used for certain built-up roofing applications. Also used to describe the combination of felts and layers of bitumen forming a single flexible unit and waterproofing system of a built-up roof covering.
Mopping
A layer of hot bitumen mopped between layers of roofing felt.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Roof deck panels (4 by 8 feet) made of narrow bits of wood, installed lengthwise and crosswise in layers, and held together with a resin glue. OSB often is used as a substitute for plywood sheets.
Penetration
A measure of the viscosity of a bitumen.
Pitch
Height from the joist to ridge divided by rafter length, which translates to rise in inches per horizontal foot or ratio of pitch. Ratio is any portion up to full pitch (24″ in 12″).
Ply
A single layer or thickness of roofing material.
Ponding
The collecting of water in shallow ponds on the top surface of roofing.
Pour Coat
The top coating of bitumen on a built-up roof.
Primer
A cut back asphalt coating of thin consistency used on concrete or metal preparatory to applying a built-up roof.
Ridge
The horizontal line where two opposite sloping sides of a roof join at the highest point of the roof, hip, or dormer.
Ridge cap
Formed shingles, shake or tile, used to cover the ridge of a building.
Roll Roofing
Any roofing material, which comes from the dealer in rolls.
Roof Drain
The termination or fitting at the roof of an interior drain or leader for draining rainwater from nominally flat roofs.
Roof Insulation
Any medium or low-density material used as a part of the roofing system to reduce heat loss through the roof.
Roof span
Distance from outer wall to opposing outer wall of a building covered with a roof.
Roofing system
The waterproof roof covering, roof insulation, vapor barrier (if used) and roof deck as an entity.
Run
The horizontal distance between the face of a wall and the ridge of the roof, being half the span for a symmetrical gable roof.
Scupper
An outlet in the wall of a building or a parapet wall for drainage of overflow water from a floor or roof directly to the outside. Special scupper drains connected to internal drains are also sometimes installed at roof and wall junctions.
Self-healing
A term used in reference to bitumen which melts with the heat from the sun’s rays, and seals over cracks that earlier formed in the bitumen from other causes.
Side Lap
The horizontal distance one shingle overlaps adjacent shingle in the same course; also the horizontal distance one sheet of roofing overlaps adjacent sheet.
Single Coverage
Method of applying roof shingles to provide only one complete layer of roof protection
Soffit
A board or sheet that extends from the fascia to the buildings siding and hides the bottom of an overhang.
Soil Stack
The main vertical pipe, which receives waste matter from all plumbing fixtures.
Step flashing
Metal shingles or plates used in a stair-step pattern under regular shingles.
Valley
The horizontal line formed along the depressed angle at the bottom of two inclined roof surfaces.
Vapor barrier
A material that prevents the passage of water or water vapor through it.
Vent;Vent pipe or Vent;Vent sleeves;
An outlet for air; A vertical pipe providing an escape for foul gases from a sanitary fixture;
Sheet metal flanged collars placed around vent pipes for the purpose of sealing-off the roofing around the vent pipe openings.
Ventilators
Devices installed on the roof for the purpose of ventilating the interior of the building.
Water Vapor
Moisture existing as a gas in air. Differences in pressures cause the vapor to do strange things such as penetrating building materials in the direction from high to low vapor pressure.